
Generally, there are four consecutive concepts under this model, which include:

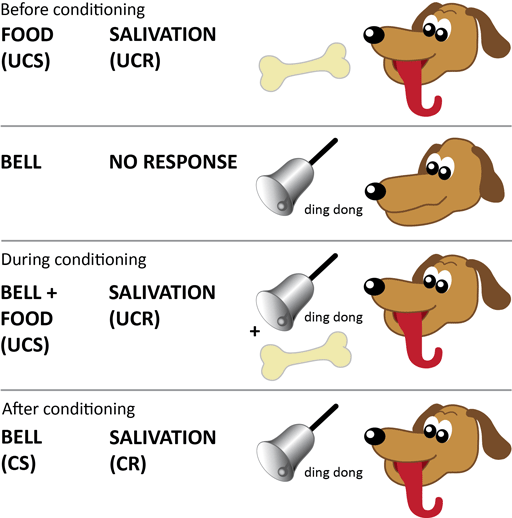
Pavlov developed a model for classical conditioning so we can have a better understanding of it. The concept of reflex, no conscious control, is incorporated in classical conditioning. One of the most common reflexes seen to us is the blinking of the eye whenever air is blown into it or a foreign object approaches it. Reflex is the involuntary behavior which comes from within. With the exposure of the organism to the stimulus, reflex results. In the case of this experiment, it was the dogs salivating when they heard the sound of the bell.In classical conditioning, the stimulus (S) triggers the response (R) of an organism. Conditioned response: This is the response after introducing the conditioned stimulus.

In the case of Pavlov’s experiment, this stimulus was the sound of the bell. However, through association with the unconditioned stimulus, it’s capable of provoking a new response.
PAVLOV CLASSICAL CONDITIONING THEORY SERIES
In order to unravel the mysteries of these new findings, Pavlov began to design a series of experiments. Pavlov concluded that his dogs had somehow associated the experiment with the imminent introduction of food. Simply s ubjecting the dogs to the conditions of the experiment was enough to provoke this reaction in them. One day, while working on this experiment, he noticed that the dogs began to salivate before he had even brought the food out. Ivan Pavlov, a Russian physiologist, was carrying out research regarding how dogs salivated in the presence of food. Secondly, we’ll talk about the components that make up this type of conditioning.
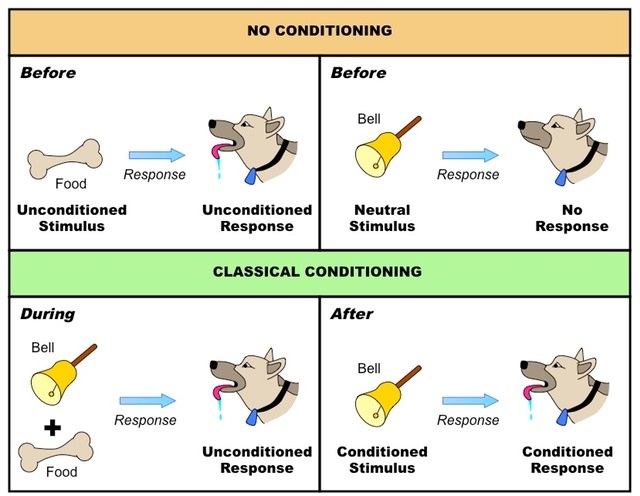
Firstly, we’ll talk about Pavlov’s experiment and his research. In order to understand classical conditioning, we’re going to discuss two aspects. This ability to associate stimuli, however different they may be, helps us in many daily situations. Thus, when the neutral stimulus is present in the absence of the other stimuli, we’ll get a similar response to the one we would get if we were to introduce the significant stimulus. Pavlov’s studies have helped us understand associative learning through classical conditioning.Ĭlassical conditioning consists of associating an initially neutral stimulus with a meaningful stimulus. Ivan Pavlov‘s experiments with dogs are very well-known in the history of psychology. People built a psychological learning theory from his small accidental discovery.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
